Research Experience
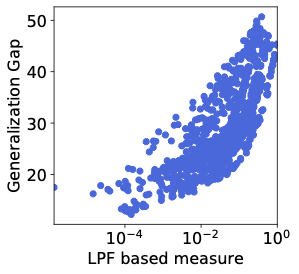
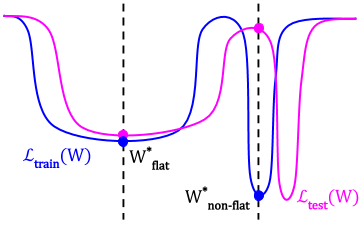
Low-Pass Filtering SGD for Recovering Flat Optima in the Deep Learning Optimization Landscape
We study the sharpness of a DL loss landscape around local minima in order to reveal systematic mechanisms underlying the generalization abilities of DL models. Our analysis is performed across varying network and optimizer hyper-parameters, and involves a rich family of different sharpness measures. We derive an optimization algorithm, relying on the low-pass filter (LPF), that actively searches the flat regions in the DL optimization landscape using SGD-like procedure. We empirically show that our algorithm achieves superior generalization performance compared to the common DL training strategies.

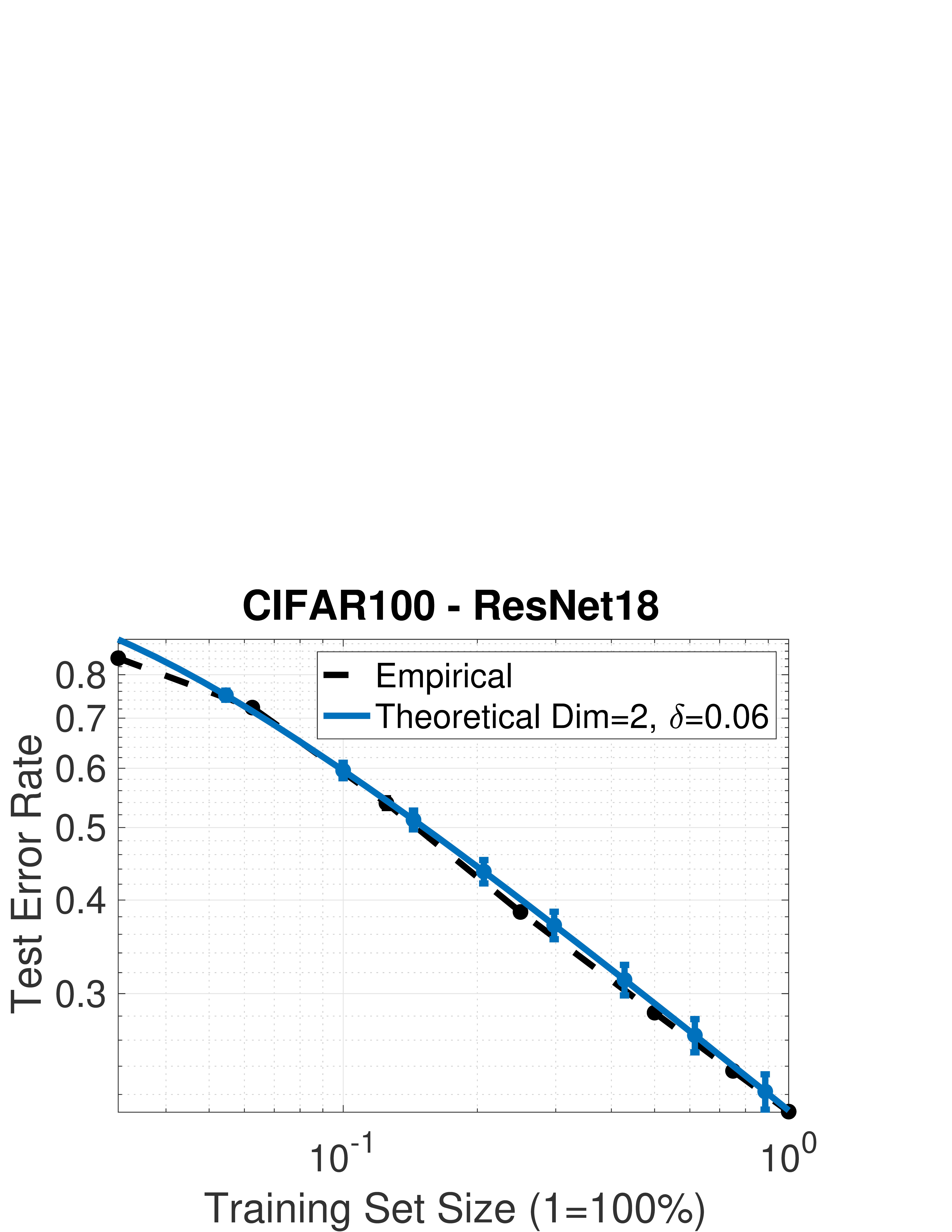
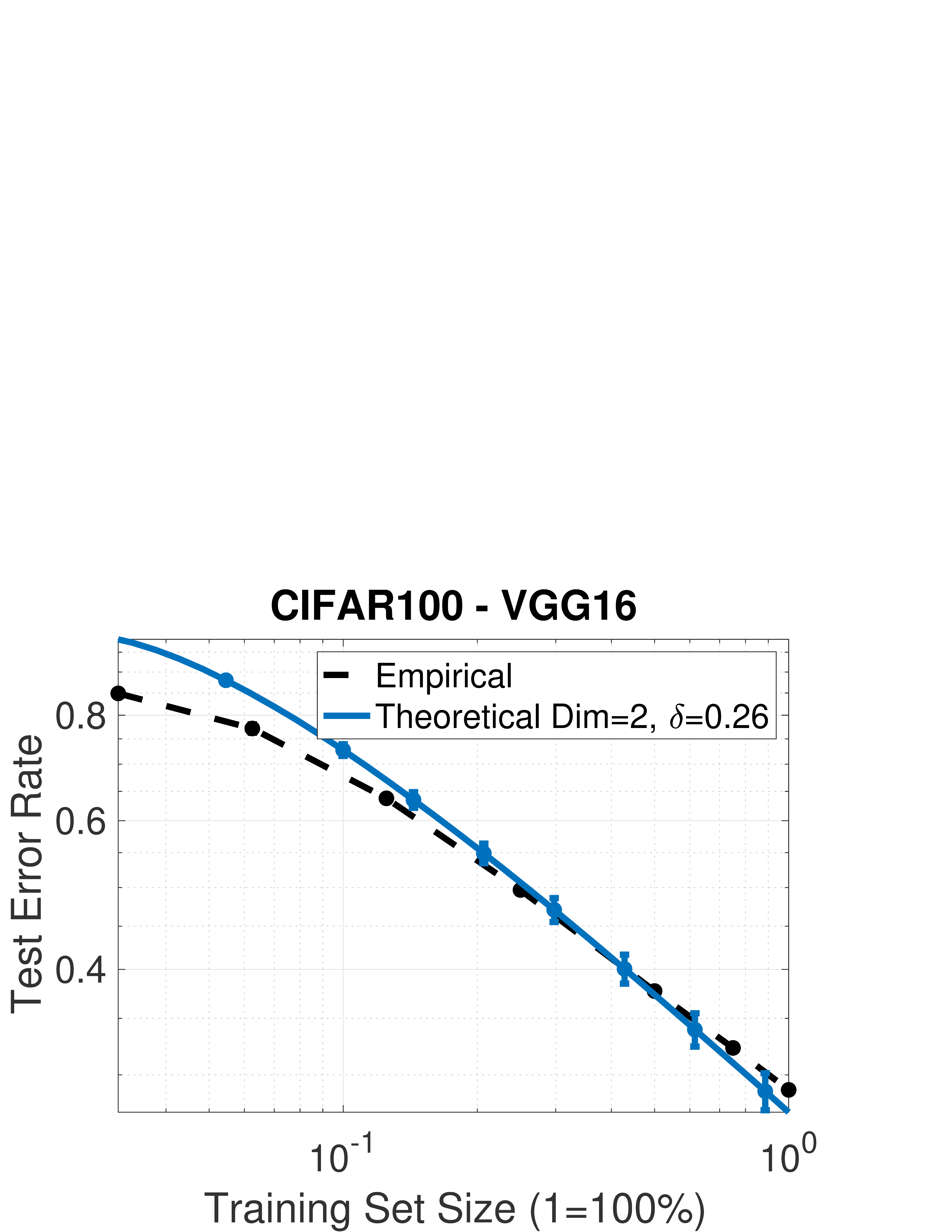
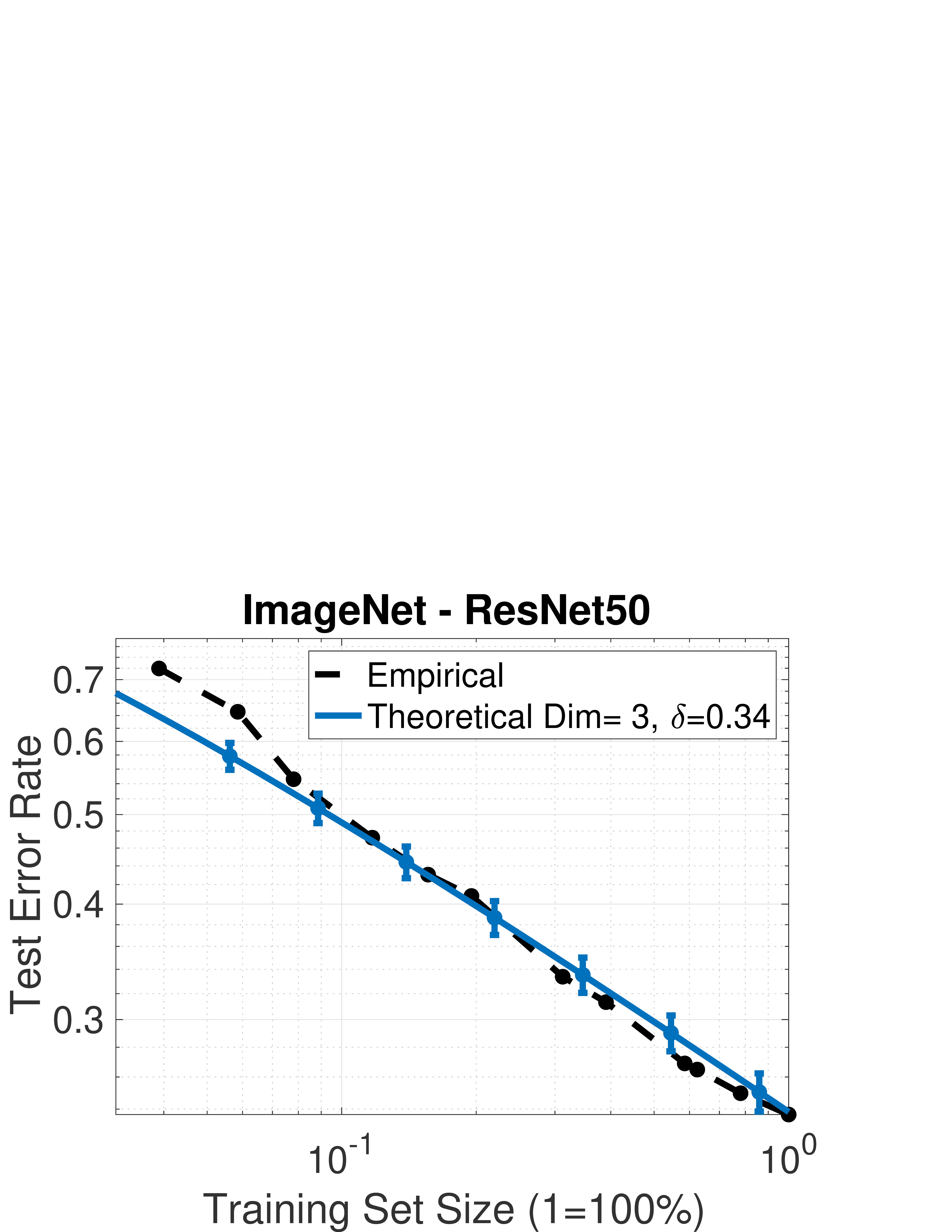
A Theoretical-Empirical Approach to Estimating Sample Complexity of DNNs
We focus on understanding how the generalization error scales with the amount of the training data for deep neural networks (DNNs). Existing techniques in statistical learning theory require a computation of capacity measures, such as VC dimension, to provably bound this error. We derive estimates of the generalization error that hold for deep networks and do not rely on unattainable capacity measures.
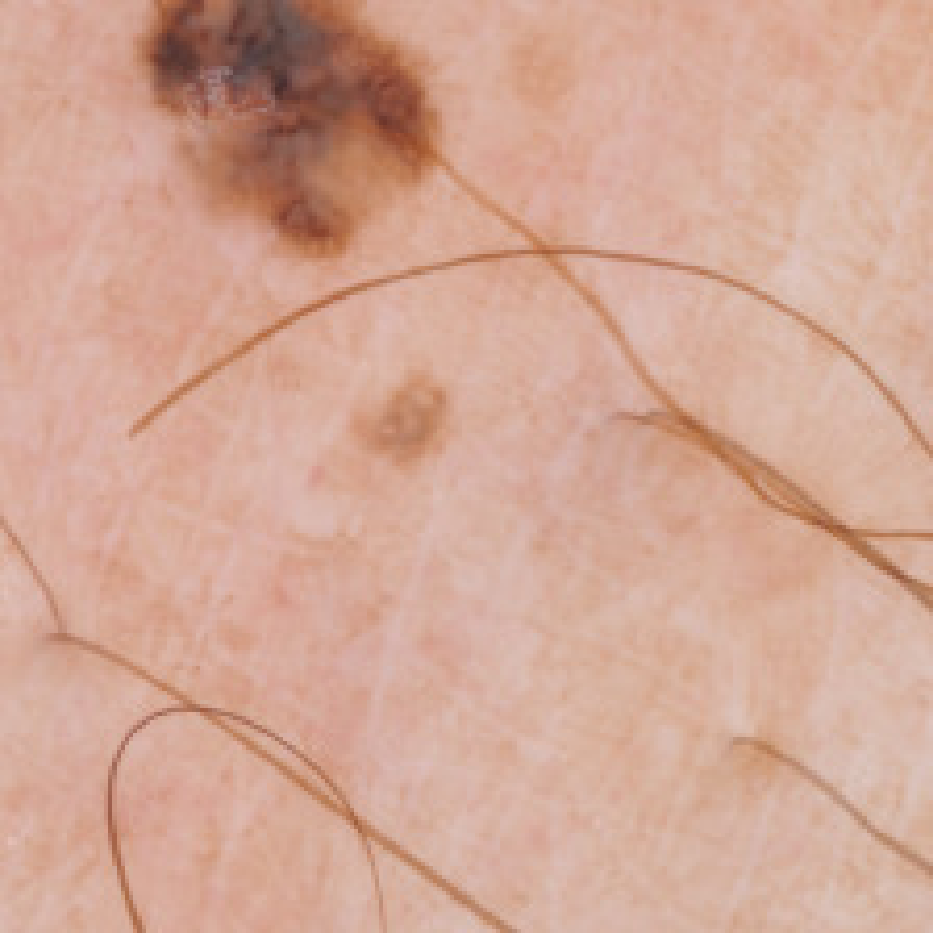
Towards Automated Melanoma Detection with Deep Learning
Melanoma is one of ten most common cancers in the US. Early detection is crucial for survival, but often the cancer is diagnosed in the fatal stage. Deep learning has the potential to improve cancer detection rates, but its applicability to melanoma detection is compromised by the limitations of the available skin lesion databases. We build deep-learning-based tools for data purification and augmentation to counter-act these limitations.
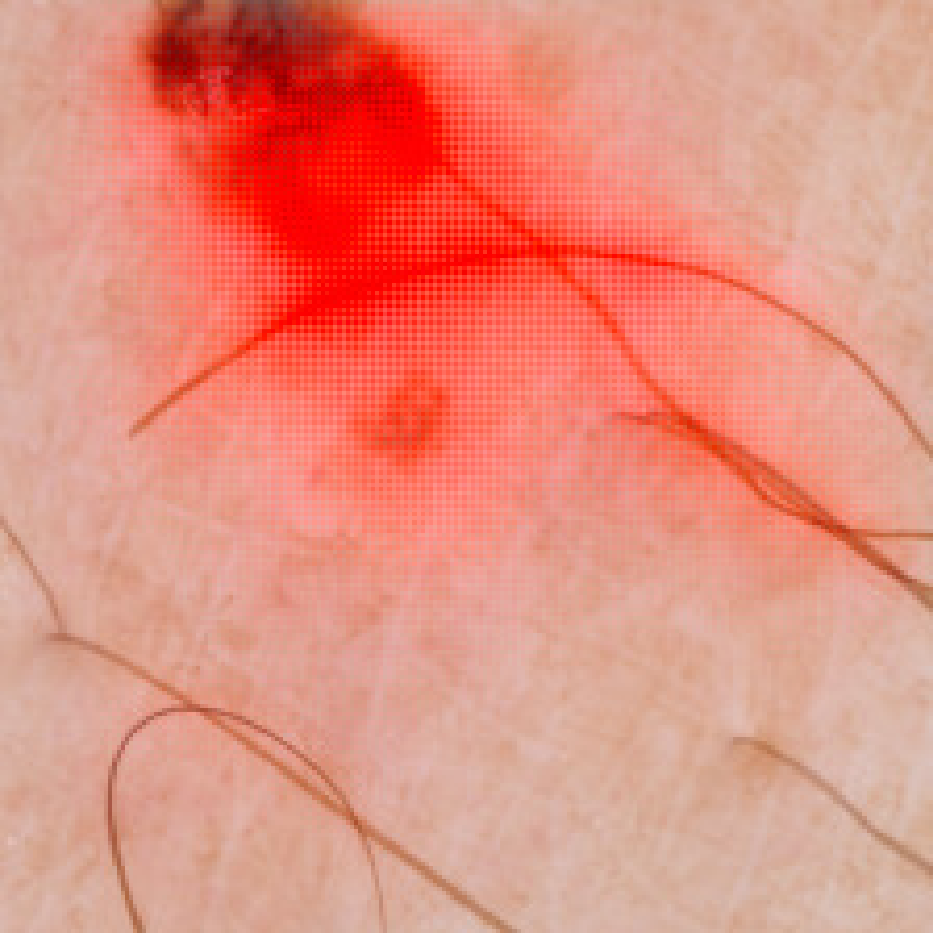
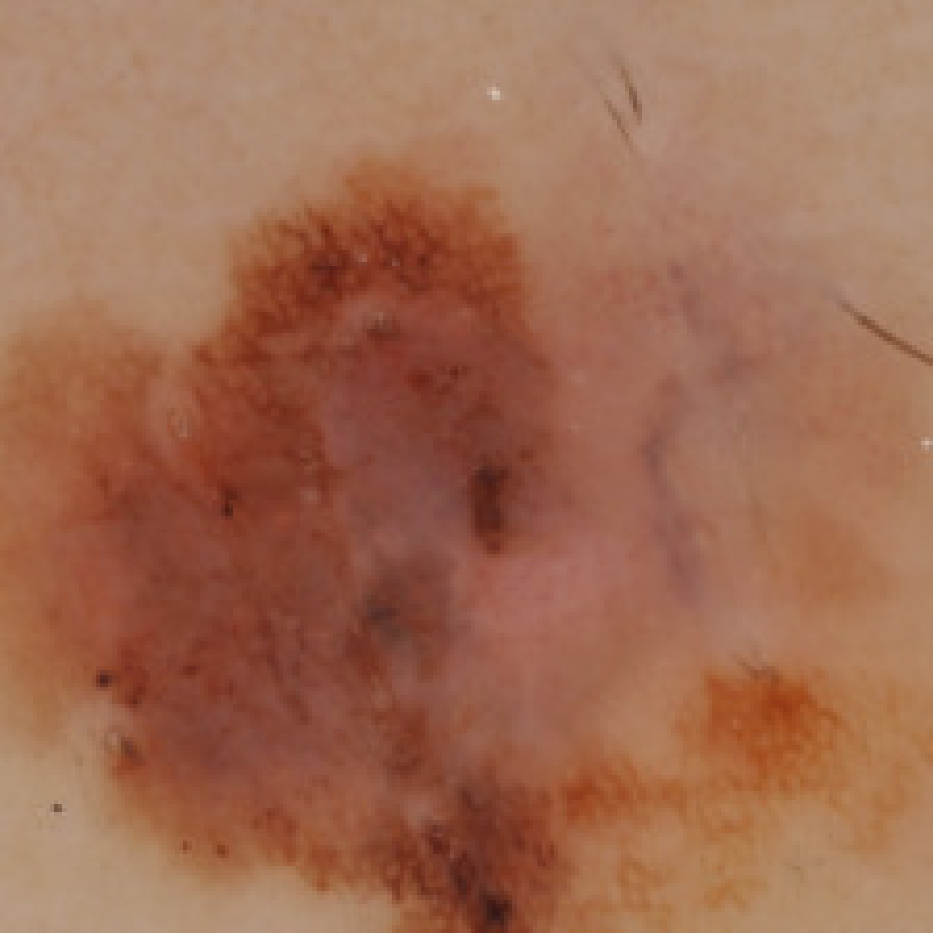
VisualBackProp for Learning using Privileged Information with CNNs
We explore the learning using privileged information paradigm and show how to incorporate the privileged information, such as segmentation masks available along with classification labels, into the training stage of convolutional neural networks. We achieve improvements of 2.4% and 2.7% over standard single-supervision model training on ImageNet and PASCAL VOC datasets.
High Frequency Ultrasound Image Segmentation and Analysis
Trained an Active Shape Model to segment brain ventricles of a mouse embryo from its high frequency 3D Ultrasound image. The shape of the brain ventricle was described using a shape context descriptor while principal component analysis was used to generate the model.
